📝 Light Question Bank
Multiple Choice questions + Case Studies + Questions
1. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light
from a point, the source is an incident on it?
(a) Concave mirror as well as a convex lens(b) Convex mirror as well as a concave lens
(c) Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other
(d) Concave mirror as well as a concave lens
Ans: (a)
2. A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror.
A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror.
The focal length of this mirror is
(a) – 30 cm
(b) – 20 cm
(c) – 40 cm
(d) – 60 cm
Ans: (-20)
3. Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
(a) When the object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of curvature
(b) When an object is kept at a distance less than its focal length
(c) When an object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
(d) When an object
Ans: (c)
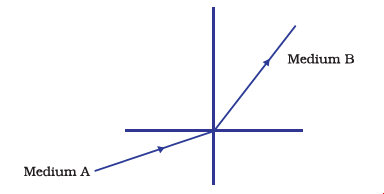
4. Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of medium B relative to medium A is
(a) `\sqrt3 / \sqrt2`
(b) `\sqrt2 / \sqrt3`
(c) `1/ \sqrt2`
(d) `\sqrt2`
Ans: (a)
5. A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in Figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be
(b) less than unity
(c) equal to unity
(d) zeero
Ans: (a)
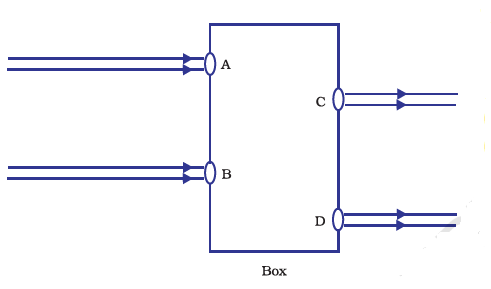
6. Beams of light are incident through holes A and B and emerge out of the box through holes C and D respectively as shown in the Figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) A rectangular glass slab
(b) A convex lens
(c) A concave lens
(d) A prism
Ans (a)
7. A mirror forms a virtual image of a real object.
(a) It must be a convex mirror.
(b) It must be a concave mirror.
(c) It must be a plane mirror.
(d) It may be any of the mirrors mentioned above.
Ans: (d)
8. The angle of incidence is the angle between
(a) the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
(b) the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
(c) the normal to the surface and the incident ray
(d) the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
Ans: (c)
9. `f = R/2` is valid
(a) for convex mirrors but not for concave mirrors.
(b) for concave mirrors but not for convex mirrors.
(c) for both convex and concave mirrors
(d) neither for convex mirrors and nor for concave mirrors.
Ans: (c)
10. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect, and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Ans: (d)
11. Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
Ans: (b)
12. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) only plane.
(b) only concave.
(c) only convex.
(d) either plane or convex
Ans: (d)
13. Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(c) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Ans: (b)
14. A full-length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using
(a) a concave mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(c) a plane mirror
(d) both concave as well as a plane mirror
Ans: (b)
15. In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed
(a) between the pole and the focus of the reflector
(b) very near to the focus of the reflector
(c) between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
(d) at the centre of curvature of the reflector
Ans: (b)
16. A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size, and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
(a) Plane, convex and concave
(b) Convex, concave, and plane
(c) Concave, plane, and convex
(d) Convex, plane, and concave
Ans: (c)
17. In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized?
(a) Concave mirror only
(b) Convex mirror only
(c) Convex lens only
(d) Concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens, and convex lens
Ans: (d)
18. A ray of light travelling in the air falls obliquely on the surface of a calm pond. It will
(a) go into the water without deviating from its path
(b) deviate away from the normal
(c) deviate towards the normal
(d) turn back on its original path
Ans: (c)
19. A ray of light goes from a medium of refractive index `n_1` to a medium of refractive index `n_2`. The angle of incidence is `i` and the angle of refraction is `r`. Then, `sin i /sin r` =
(a) `n_1`
(b) `n_2`
(c) `n_1/n_2`
(d) `n_2/n_1`
Ans: (d)
20. Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(c) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Ans: (b)
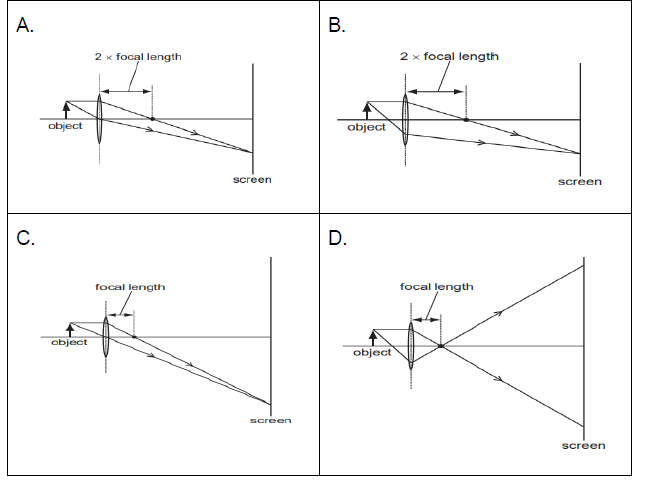
21. Which diagram shows the image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens?
Ans: (c)
22. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
A. Concave mirror as well as convex lens.
B. Convex mirror as well as concave lens.
C. Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each others.
D. Concave mirror as well as concave lens.
Ans: (A)
23. Consider these indices of refraction: glass: 1.52; air: 1.0003; water: 1.333. Based on the refractive indices of three materials, arrange the speed of light through them in decreasing order.
A. The speed of light in water `>` the speed of light in air `>` the speed of light in glass.
B. The speed of light in glass `>` the speed of light in water `>` the speed of light in air.
C. The speed of light in air `>` the speed of light in water `>` the speed of light in glass.
D. The speed of light in glass `>` the speed of light in air `>` the speed of light in water.
Ans: (c)
Examine the above figure and state which of the following option is correct? [one small box in the figure is equal to 1 cm]
A. The mirror has a focal length of `-6` cm and will produce an image of magnification `+1`.
B. The mirror has a focal length of `-3` cm and will produce an image of magnification `-1`.
C. The mirror has a focal length of `-3` cm and will produce an image of magnification `+1`.
D. The mirror has a focal length of `-6` cm and will produce an image of magnification `-1`.
Ans: (B)
The angle of incidence from air to glass at the point O on the hemispherical glass slab is
A. 45°
B. 0°
C. 90°
D. 180°
Ans: (B)
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following-
i. the image of the object will be a virtual one.
ii. the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
iii. the image of the object will be inverted.
iv. this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
A. i and ii
B. i and iii
C. ii, iii and iv
D. i, ii, iii and iv
Ans: (c)
In the above diagram, light is travelling through different media. It is noted by a scientist that `∠1= ∠3= ∠4` but `∠2 <∠1`. Which of the following statement would be correct?
A. Medium 1 is denser than medium 3 but its density is equal to medium 2.
B. Medium 2 is the rarest medium.
C. Medium 3 is denser than medium 1.
D. Medium 1 and 3 are essentially the same medium, but medium 2 is denser than 1 and 3
Ans: (D)
26. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length of 0.25 m
(b) A convex lens has –4 dioptre power having a focal length of 0.25 m
(c) A concave lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length of 0.25 m
(d) A concave lens has –4 dioptre power having a focal length of 0.25 m
Ans: (a)
27. A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as shown in the Figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) Concave lens
(b) Rectangular glass slab
(c) Prism
(d) Convex lens
Ans: (d)
28. The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in Figure 10.5. Which one of them is correct?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans: (b)
29. Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in Figure.
30 Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a lens shown in Fig.
Ans: (a)
31. In a convex mirror, reflection of light takes place at:
a) a flast surface
b) a bent in surface
c) a bulging out surface
d) an uneven surface
32. A diverging mirror is:
a) a plane mirror
b) a convex mirror
c) a concave mirror
d) a shaving mirror
33. The focal length of a spherical mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm is:
a) 10 cm
b) 15 cm
c) 20 cm
d) 30 cm
★★★★★★
Assertion & Reason
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but Reason is true.
1. Assertion: The focal length of the convex mirror will increase if the mirror is placed in water.
Reason: The focal length of the convex mirror of radius R is equal to, `f = R/2`
2. Assertion: An object is placed at a distance of `f` from a convex mirror of focal length `f`, its image will form at infinity.
Reason: The distance of an image in a convex mirror can never be infinity.
★★★★★★★
Q. A convex mirror used for rear-view on an automobile has a radius of curvature of `3.00 m`. If a bus is located at `5.00 m` from this mirror, find the position, nature, and size of the image.
Ans: `v` = + 1.15 m , `m = + 0.23`
Q. An object, `4.0 cm` in size, is placed at `25.0 cm` in front of a concave mirror of focal length `15.0 cm`. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image? Find the nature and the size of the image.
Ans: `v = – 37.5 cm, h^' = – 6.0 cm`
Q. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at `10 cm` in front of it. Where is the image located?
Ans: `v = -30 cm`
Q. Size of the image of an object by a mirror having a focal length of 20
cm is observed to be reduced to 1/3rd of its size. At what distance
the object has been placed from the mirror? What is the nature of
the image and the mirror?
Ans: `u =-80`cm, image is real
and inverted. The mirror is concave.
Q. An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Ans: `v` = + 6 cm
Q. An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature, and size.
Ans: `v` = + 8.75 cm, `h^'` = 2.1 cm
Q. An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed so that a sharply focussed image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Ans: `v` = `-54` cm, `h^'` = `-14.0` cm
Q. A 2 cm high object is placed at a distance of 32 cm from a concave mirror. The image is real, inverted and 3 cm in size. Find the focal length of the mirror and the position of the image.
Ans: `f` = `- 19.2` cm
Q. A concave mirror forms an inverted image of an object placed at a distance of 12 cm from it. If the image is twice as large as the object, where is it formed?
Ans: `v` = `-24` cm
Q. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex mirror when an object is placed
(a) at infinity
(b) at finite distance from the mirror
Q. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave mirror when an object is placed
(a) between pole and focus of the mirror
(b) between focus and centre of curvature of the mirror
(c) at centre of curvature of the mirror
(d) a little beyond centre of curvature of the mirror
(e) at infinity
Q. Under what condition in an arrangement of two plane mirrors, incident ray and reflected ray will always be parallel to each other, whatever may be angle of incidence. Show the same with the help
of diagram.
Q. A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as a real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
Q. Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following cases, when the image formed is virtual and erect in each case.
(a) Object is placed between device and its focus, image formed is enlarged and behind it.
(b) Object is placed between the focus and device, image formed is enlarged and on the same side as that of the object.
(c) Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between focus and optical centre on the same side as that of the object.
(d) Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between pole and focus, behind it.
★★★★★★★
Refractive Index (Numericals)
Q. A ray of light travelling in the air falls on the surface of a transparent slab. The ray makes an angle of 45° with the normal to the surface. Find the angle made by the refracted ray with normal within the slab. Refractive index of the material of the slab = `\sqrt2`
Ans: `r = 30°`
Q. A ray of light travelling in air is incident on the plane surface of a transparent medium. The angle of the incidence is 45° and the angle of refraction is 30°. Find the refractive index of the medium.
Ans: `\sqrt 2`
`
Q. A ray of light travelling in the air falls on the surface of a rectangular slab of plastic material whose refractive index is 1.6. If the incident ray makes an angle of 53° with the normal, find the angle made by the refracted ray with the normal ( sin53° = `4/5`).
Ans: `r = 30°`
Q. A ray of light travelling in the air falls on the surface of transparent material at an angle of 45° to the normal. It bends by 15° after refraction. Find the refractive index of the material.
Ans: `\sqrt2`
Q. Light is incident on a clear plastic block at an angle of 45°. The speed of light in the plastic is `c/\sqrt 2`, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum. Find the angle of refraction.
Ans: 30°
Q. Find the refractive index of air with respect to water ( `n_{water} = 4/3`).
Ans: `3/4`
Q. A diamond ( `n = 2.42`) is dipped in a liquid of refractive index 1.4. Find the refractive index of diamond with respect to the liquid.
Ans: 1.73
Q. Light enters from air to glass having a refractive index of 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in a vacuum is `3 × 10^8 m s^{–1}`.
★★★★★★★★
Q. A concave lens has focal length of 15 cm. At what distance should the object from the lens be placed so that it forms an image at 10 cm from the lens? Also, find the magnification produced by the lens.
Ans: `u = 30` cm, m = + 0.33. The positive sign shows that the image is erect and virtual. The image is one-third of the size of the object.
Q. A 2.0 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position, and size of the image. Also, find its magnification.
Ans: `v = 30` cm, The positive sign of v shows that the image is formed at a distance of 30 cm on the other side of the optical centre. The image is real and inverted. `h^' = - 4.0` cm, m = `-2`. The negative signs of m and h
show that the image is inverted and real.
Q. An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size, and nature of the image formed.
Q. A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Q. How are the power and focal length of a lens related? You are provided with two lenses of focal length 20 cm and 40 cm respectively. Which lens will you use to obtain more convergent light?
Q. Define power of a lens. What is its unit? One student uses a lens of focal length 50 cm and another of –50 cm. What is the nature of the lens and its power used by each of them?
More questions will be updated soon.









Very good questions 👍👍👍
ReplyDeleteNice questions sir ✌
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteVery critical questions
Very hard
Very helpful for students
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟👍👌🔒🗝️
Very very hard question for students
ReplyDeleteThanku for
You are great notice and videos
For students
🌟🌟👁️🌟🌟👍👁️👍🔒🗝️