Heredity and Variation
Introduction
We have seen that reproductive processes give rise to new individuals that are similar, but subtly different. If we observe a field of sugarcane we find very few variations among the individual plants. But in a number of animals including human beings, which reproduce sexually, quite distinct variations are visible among different individuals.
Accumulation of Variation during Reproduction
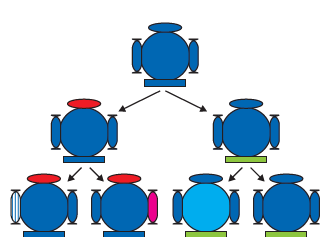
👉 Inheritance from the previous generation provides both a common basic body design and subtle changes in it, for the next generation.What would happen when this new generation, in its turn, reproduces?
The second generation will have differences that they inherit from the first generation, as well as newly created differences.
The figure would represent the situation if a single individual reproduces, as happens in asexual reproduction. If one bacterium divides, and then the resultant two bacteria divide again, the four individual bacteria generated would be very similar. There would be only very minor differences between them, generated due to small inaccuracies in DNA copying. However, if sexual reproduction is involved, even greater diversity will be generated.
Do all these variations in a species have equal chances of surviving in the environment in which they find themselves?
Obviously not. Depending on the nature of variations, different individuals would have different kinds of advantages. Bacteria that can withstand heat will survive better in a heat wave.
Heredity
The transmission of characters (or traits) from parents to their offspring is called heredity.
The most obvious outcome of the reproductive process still remains the generation of individuals of similar design. The rules of heredity determine the process by which traits and characteristics are reliably inherited.
Rules for the Inheritance of Traits – Mendel’s Contributions
Gregor Mendel was the first scientist to make a systematic study of patterns of inheritance that involved the transfer of characteristics from parents to progeny.

👍👍👍👍
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDeleteAwesome work 👍👌👍👌👍👌
ReplyDelete